

Standard precautions, particularly aseptic technique, form the basis of safe injection practices. Needle-stick and Sharps Injury Preventionīreaches in safe injection, infusion and medication vial handling practices have resulted in transmission of HIV and viral hepatitis and in some cases caused outbreaks of disease. Management of the critical aseptic field requires sterilized equipment to be placed in the aseptic field sterile gloves are required to maintain asepsis.
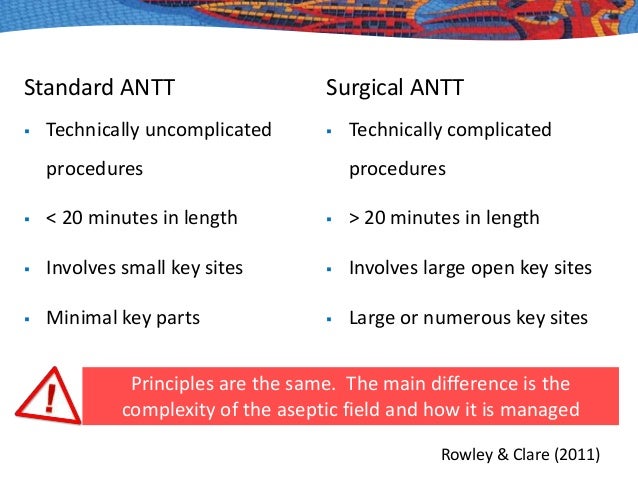
Invasive procedures require a large aseptic working area. Key parts/sites are large or numerous and can't be easily protected by covers or caps or can't be handled with a non-touch technique. protection of key parts by the use of syringe caps, sheathed needles, covers or packaging.Īsepsis of the immediate procedure environment is therefore promoted by general aseptic field management. Key parts are easily protected by critical micro aseptic fields and non-touch technique e.g. Standard aseptic fields that promote asepsis are used when Reducing pathological organisms by using non-touch technique (clean technique). Asepsis can be explained in different levels Standard Aseptic technique and Medical Asepsis Sterile single-use equipment or instruments must be used according to manufacturer's instructions and in such a way that the sterility of the item is maintained. PPE must fit the individual user, and it is up to the employer to ensure that all PPE are available in sizes appropriate for the workforce that must be protected.Īseptic technique is a set of practices aimed at minimising contamination and is used to protect the patient from infection during procedures. This will affect, for example, whether a gown or apron is selected for PPE, or, if a gown is selected, whether it needs to be fluid resistant, fluid proof, or neither. Second is the durability and appropriateness of the PPE for the task. PPE selection, in particular the combination of PPE, also is determined by the category of isolation precautions a patient is on. This is determined by the type of activity, such as touch, splashes or sprays, or large volumes of blood or body substance that might penetrate the clothing. First is the type of anticipated exposure. When you are selecting PPE, consider three key things 
Further information is available at ACSQHC.
Selections should be guided by the anticipated type and amount of exposure to blood and body substances and the likely transmission route of microorganisms.
EXAMPLES OF MEDICAL ASEPSIS SKIN
soap, disposable towels) are consistently available.Īppropriate PPE should be selected to prevent contamination of skin and/or clothing. Provide conveniently located dispensers of alcohol-based hand rub where sinks are available, ensure that supplies for hand washing (i.e.Provide tissues and no-touch receptacles for used tissue disposal.Healthcare facilities should ensure the availability of materials for adhering to Respiratory Hygiene/Cough Etiquette in waiting areas for patients and visitors.

hand washing with soap and water, alcohol-based hand rub, or antiseptic hand wash) after having contact with respiratory secretions and contaminated objects/materials.
Use the nearest waste receptacle to dispose of the tissue after use. If you don't have a tissue, cough or sneeze into your elbow. Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing. The following measures to contain respiratory secretions are recommended for all individuals A Health Organisation should encourage and enable patients, visitors and Health Workers to perform respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette and provide appropriate resources to support these behaviours. To minimise the risk of transmission of infection to others, everyone entering, visiting or working within a Health Organisation presenting with the signs and symptoms of respiratory infection should practise respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette. Needle-stick and Sharps Injury Prevention. Standard Precautions comprise the following measures:. These evidence-based practices are designed to both protect and prevent spread of infection among patients and healthcare personnel. Standard Precautions represent the minimum infection prevention measures that apply to all patient care, regardless of suspected or confirmed infection status of the patient, in any setting where healthcare is delivered.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
